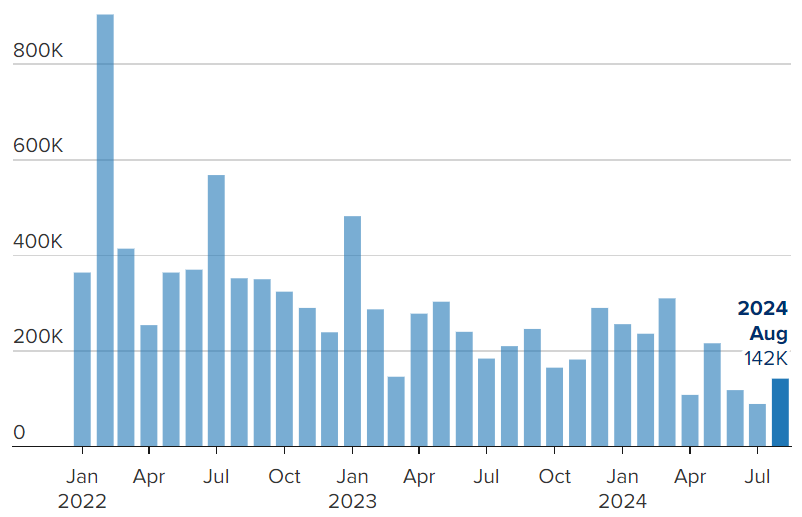
The U.S. job market in August 2024 delivered a mixed bag of results, revealing both optimism and concerns for the country’s economic trajectory. With payroll additions missing the mark but the unemployment rate showing a positive downward trend, the latest jobs report sheds light on the state of the labor market and its broader implications for the economy.
What the August Jobs Report Reveals
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) announced that payrolls grew by 142,000 in August 2024, falling short of the anticipated 180,000 jobs. Although the growth was slower than expected, the unemployment rate dropped to 4.2%, signaling that fewer people are actively seeking work.
Key Data Points:
- Jobs added in August 2024: 142,000
- Expected job growth: 180,000
- Unemployment rate: 4.2% (previous month: 4.4%)
- Sector highlights: Healthcare, professional services, and government were the primary contributors to job growth, while retail and manufacturing experienced declines.
A Closer Look at Payroll Growth
The jobs report for August shows a deceleration in hiring compared to earlier months, reflecting employers’ cautious approach amid economic uncertainties. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policies, inflation concerns, and global economic factors continue to play significant roles in shaping these trends.
What Sectors Saw the Most Growth?
Healthcare and Social Assistance
The healthcare sector remains a bright spot in the economy, adding around 50,000 jobs in August. Hospitals, outpatient care centers, and nursing facilities are seeing consistent demand, largely driven by the aging population and increased health care needs post-pandemic.
Professional and Business Services
Adding 32,000 jobs, the professional and business services sector has demonstrated steady growth. This includes roles in accounting, consulting, and technical services, which are essential for businesses adapting to technological advancements and regulatory changes.
Government Jobs
Government employment rose by 25,000, with most of the gains coming from local education sectors. As schools prepare for the academic year, hiring has spiked to meet the increased demand for teachers and administrative staff.
Areas of Decline: Retail and Manufacturing
While some sectors thrive, others continue to face challenges. Retail employment declined by 28,000 jobs in August, as shifts toward e-commerce and automation displace traditional retail workers. Meanwhile, manufacturing lost 18,000 jobs, reflecting global supply chain disruptions and the rising cost of raw materials.
What Does the Unemployment Rate of 4.2% Signify?
Although the unemployment rate dropped to 4.2%, it doesn’t necessarily mean more people are getting jobs. The labor force participation rate, which measures the number of people actively seeking employment, also declined slightly, indicating that some individuals have left the job market altogether.
Unemployment by Demographics
- Men: 4.0%
- Women: 4.3%
- Youth (ages 16-24): 8.6%
- Black or African American: 5.8%
- White: 3.5%
Factors Influencing Job Market Performance
Federal Reserve’s Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve’s efforts to control inflation through interest rate hikes continue to impact hiring. While higher interest rates aim to curb inflation, they also slow down business expansions and investments, limiting the demand for new hires.
Inflation Concerns
Inflation remains a primary concern for both businesses and workers. Rising prices of goods and services squeeze corporate profits, leading many companies to adopt a cautious approach to hiring. Consumers, on the other hand, feel the pinch, which affects their purchasing power and, ultimately, businesses’ sales.
Global Economic Conditions
International factors, such as the ongoing war in Ukraine, global supply chain bottlenecks, and energy prices, further complicate the domestic job market. These conditions cause uncertainties that make both large corporations and small businesses hesitant to hire.
How the Jobs Report Affects Markets
The August jobs report had a noticeable impact on financial markets. The lower-than-expected job growth raised concerns about the economy’s resilience, causing a slight dip in the stock market. However, the decrease in the unemployment rate provided a silver lining, preventing more significant losses.
Stock Market Reaction
The S&P 500 fell by 0.4% following the report’s release, reflecting investors’ concerns about slower economic growth. Meanwhile, the bond market saw gains as investors sought safe-haven assets amidst economic uncertainty.
What’s Next for the Labor Market?
Looking ahead, economists predict that the U.S. labor market will continue to experience moderate growth for the rest of 2024. However, much will depend on the Federal Reserve’s future actions and the trajectory of inflation.
Predictions for Q4 2024
- Job growth may average between 100,000 to 150,000 per month.
- The unemployment rate could hover around 4.0% to 4.2%.
- Sectors like healthcare, technology, and education are expected to remain strong contributors to job growth.
FAQs about the August 2024 Jobs Report
1. Why did payroll growth in August miss expectations?
Payroll growth in August fell short due to cautious hiring by businesses facing inflation, higher interest rates, and global uncertainties. Many companies have adopted a “wait and see” approach before expanding their workforce.
2. What sectors added the most jobs in August 2024?
Healthcare, professional services, and government sectors led the job gains, while retail and manufacturing experienced declines.
3. How does the unemployment rate reflect the current job market?
The unemployment rate dropped to 4.2%, indicating fewer people are actively seeking work. However, a decrease in labor force participation shows that some individuals have exited the job market.
4. How are inflation and interest rates impacting hiring?
High inflation and rising interest rates make businesses more cautious about expansion, limiting their ability to hire new workers.
5. What can we expect from the labor market in the coming months?
Experts predict moderate job growth for the rest of 2024, particularly in healthcare, technology, and education, but factors like inflation and the Federal Reserve’s policies will continue to influence the market.